Trauma care is critical in emergency medicine, where timely and accurate diagnosis is paramount. With its advanced imaging techniques, radiology plays a crucial role in trauma care by providing detailed insights into injuries, aiding in swift decision-making, and improving patient outcomes. This article delves into the essential functions of radiology in trauma care and how it has revolutionized the field.
The Importance of Radiology in Initial Assessment
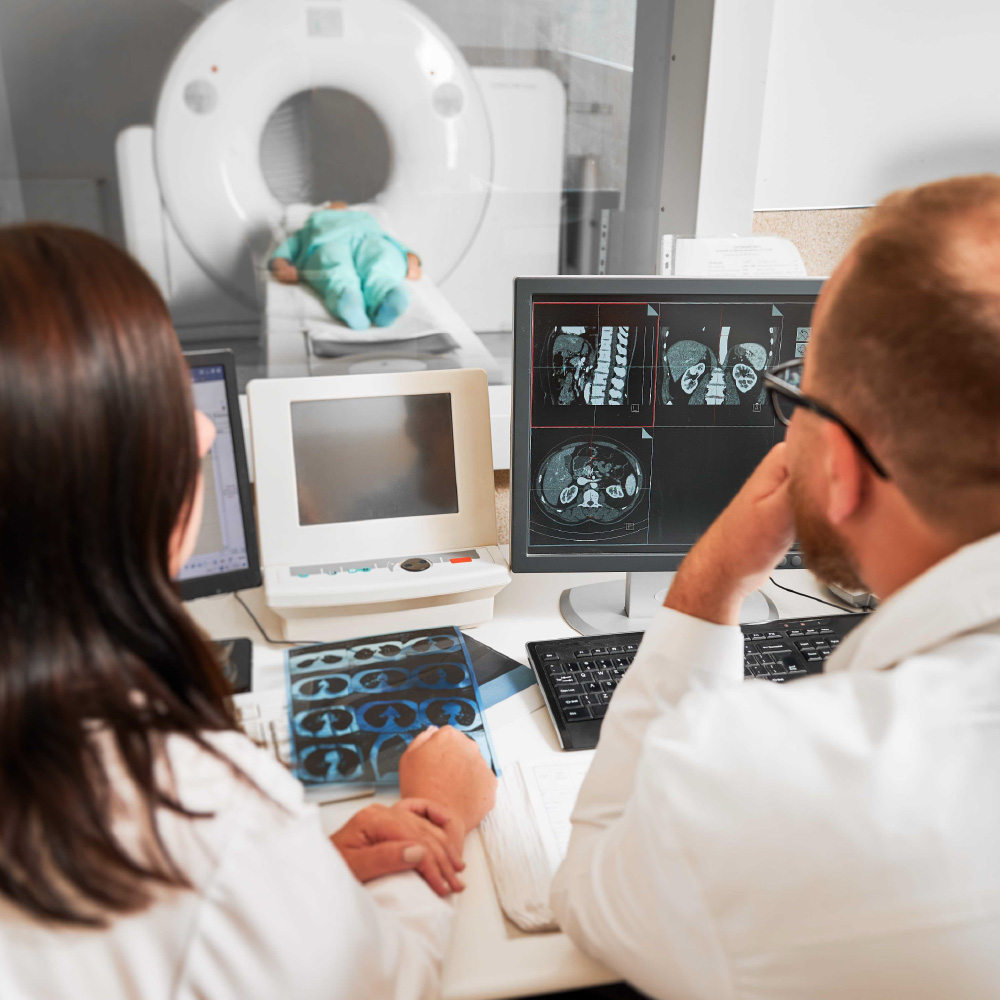
Radiology is integral to the initial assessment of trauma patients. When a patient arrives in the emergency department following an injury, time is of the essence. Radiological imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds are among the first diagnostic tools used. These imaging methods allow medical professionals to quickly identify internal injuries that might not be apparent through physical examination alone.
For example, a CT scan can reveal the extent of head injuries, internal bleeding, or organ damage within minutes, providing critical information that guides the next steps in treatment. In many cases, the speed and accuracy of radiological assessments can mean the difference between life and death, making radiology an indispensable part of trauma care.
Advanced Imaging Techniques and Their Applications
In trauma care, advanced imaging techniques offer detailed insights essential for effective treatment. Computed Tomography (CT) scans are particularly valuable, as they provide cross-sectional images of the body, allowing for a comprehensive view of injuries. This is especially important in cases of blunt trauma, where internal injuries may not be immediately obvious.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is another crucial tool for soft tissue injuries and neurological damage. Unlike CT scans, MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of organs and tissues. This makes it ideal for detecting spinal cord injuries, brain trauma, and ligament damage. In cases of severe trauma, where multiple areas of the body are affected, MRI can provide a more detailed assessment than other imaging techniques.
The Role of Radiology in Surgical Planning
Radiology is also vital in surgical planning for trauma patients. Once the initial assessment has been completed, surgeons rely on detailed radiological images to plan their approach. For instance, radiological images can help surgeons determine the most effective surgical techniques and anticipate potential complications in complex fractures or internal bleeding.
Interventional radiology, a subspecialty within radiology, has become increasingly important in trauma care. This technique involves minimally invasive imaging-guided procedures, such as inserting catheters to stop internal bleeding or draining abscesses. These procedures can be life-saving, particularly in patients who are too unstable for traditional surgery. By reducing the need for open surgery, interventional radiology can also speed up recovery times and reduce the risk of complications.
Radiology in Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
The role of radiology extends beyond initial diagnosis and surgical planning; it is also crucial in monitoring and follow-up care. After surgery or other interventions, radiological imaging is used to monitor the healing process and detect any complications that may arise. For example, follow-up CT scans or X-rays can reveal whether fractures are healing properly or if there is any ongoing internal bleeding.
In addition, radiology plays a significant role in the long-term follow-up of trauma patients. Some injuries, such as traumatic brain injuries or spinal cord damage, may require ongoing monitoring to assess the extent of recovery or the development of secondary complications. Through regular imaging, healthcare providers can track the progress of recovery and make informed decisions about further treatment or rehabilitation.
Innovations in Radiology Impacting Trauma Care
The field of radiology is continuously evolving, with innovations that have a profound impact on trauma care. One such innovation is the development of portable imaging devices. These allow for immediate imaging at the patient’s bedside, which is particularly useful in emergencies where time is critical. Portable X-rays, for example, can be used in the emergency room or even in the field, providing rapid diagnosis and enabling swift intervention.
Another significant advancement is integrating artificial intelligence (AI) in radiology. AI algorithms can quickly analyze radiological images and identify abnormalities, assisting radiologists in making faster and more accurate diagnoses. This is particularly valuable in trauma care, where the speed of diagnosis can directly impact patient outcomes. By automating the analysis process, AI allows radiologists to focus on more complex cases and reduce the time to treatment.
Conclusion: Radiology as a Cornerstone of Trauma Care
Radiology has established itself as a cornerstone of trauma care, providing critical support in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of trauma patients. Radiological imaging ensures that injuries are accurately identified and appropriately managed from the initial assessment to follow-up care. As technology advances, the role of radiology in trauma care will only become more integral, enhancing the ability of healthcare providers to deliver timely and effective care to those in need.